
Knowledge Area

Folate or Vitamin B9 (Folic acid)
Folic acid is also recognized as a vitamin for pregnancy. It plays a very important role in cell division and development. The nutrient, also known as vitamin B9, is thus indispensable for a new life without complications.
If you are in the conception process or are pregnant, it is usually recommended that you additionally take at least 400ug of folic acid per day. This vitamin is vital for the optimum growth of the embryo in the first few months of pregnancy. The main reason you need to take folic acid supplements during pregnancy is sufficient absorption of folic acid is typically difficult during pregnancy via food. The vitamin is not very heat resistant and can be quickly destroyed in the preparation of a meal.
The most important folic acid dietary sources are:
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Yeast
- Spinach
- Brussels
- Oranges
- and legumes
Why you need Folic acid?
- Folic acid strengthens the mother and child immune system.
- It also combats unnecessary fatigue in cooperation with adequate vitamin B12.
So:
Do not give up a dietary supplement containing folic acid during pregnancy in any condition.

Iodine
Why you need Iodine
The Iodine containing hormones play an important role in regulating the growth and development of:
- Nervous system
- Skeleton system
- Muscles
- and Organs
These hormones also have a strong effect on intelligence and mental development. Iodine is also important for a healthy energy balance and protection of the skin. The hormone development of the own thyroid gland starts in the fetus at the beginning of the third month of pregnancy.
Your baby always depends on the iodine you ingest.
Iodine is found in a few foods only. The mineral is present in fish and iodine salt, for example, and in very little quantities in some dairy products.
You should also ensure adequate intake of iodine during your pregnancy and lactation via a food supplement to enable your child to develop without any complications.
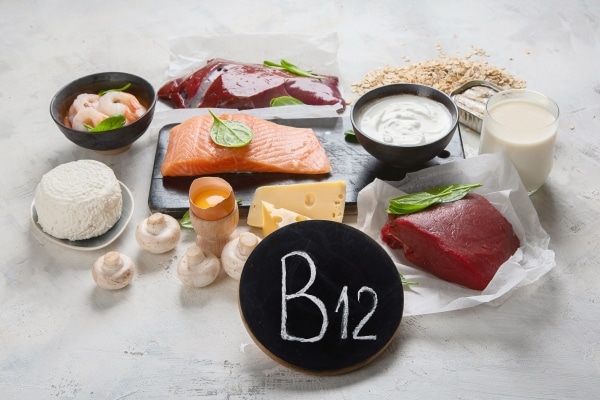

Vitamin B12
Deficiency of vitamin B12 is one of the most common mineral deficiencies.
Why we need B12
This vitamin is essential for the nervous system function and for the error-free formation of blood. Furthermore, without adequate vitamin B12, pregnancy vitamin folic acid can not function correctly.
Vitamin B12 deficiency often occurs, particularly in the people who take the diet low in meat, vegetarian, or even in vegan. The vitamin is mostly found in animal products such as:
- Meat
- Fish
- Eggs
- and Milk
However, many people who consume meat still experience a deficiency in vitamin B12.
The additional vitamin B12 intake during pregnancy and lactation is strongly recommended to help your nervous system and your infant’s growth. Your immune system would also benefit from an adequate vitamin supply.

Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is also known as a sun vitamin for many people. This is because the body can produce this vitamin autonomously under sunlight. This works as follows:
As you exposed the sunlight, UV-B rays reaching the skin and producing the provitamin D3, which are used to produce pre-vitamin D3 às, reach the bloodstream. From the bloodstream, pre-vitamin D3 transported into the liver and kidney, where it is converted into the active vitamin D
Tiny amounts of vitamin D3 are also present in certain foods. For example, these include:
- Liver
- Eggs
- Butter
- fatty types of fish
- and edible mushrooms
However, sunlight should satisfy 80-90% of the need for vitamin D3.
Many people have vitamin D3 deficiency. This is partially because a substantial part of the population is not exposed to the light. Also, the blocking effect of sunscreens is also responsible, which can prevent vitamin production as early as 20 SPFs.
Why is vitamin D3 especially essential during pregnancy?
It supports the immune and hormonal systems and supplies the body with calcium (particularly essential for building teeth, bones, and muscles). Moreover, some studies indicate that vitamin D3 may have a beneficial impact on fertility in both sexes.
Women taking ample vitamin D3 are less likely to develop gestational diabetes. In children whose moms obtain sufficient vitamin D3, the development of allergies is also shown to be lower.